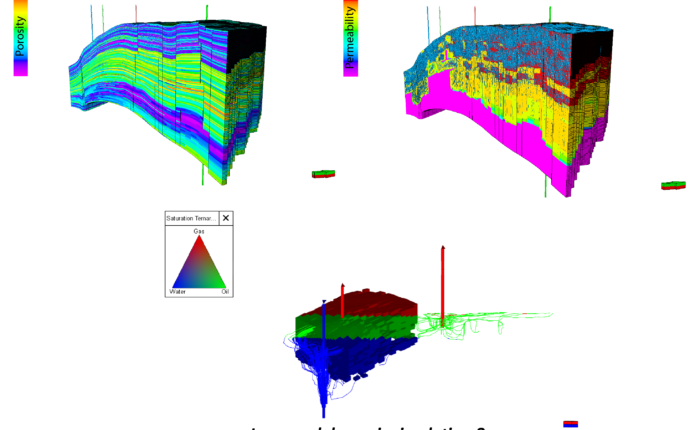
Nuclear processes are routinely used in the fields of energy, industry, medicine, and research, however these activities create a by-product in the form of radioactive nuclear waste. Since the waste generated is harmful to life and the environment, it needs to be managed safely for the long-term (~200,000 years). A deep geological repository is internationally recognised as the safest long-term solution for the disposal of this waste.
Since 2019, Ad Terra Consultancy has been working closely with Nagra (the Swiss National Cooperative for the Disposal of Radioactive Waste) to conduct geoscientific investigations in both shallow and deep boreholes to produce detailed analyses of the underground geological environment. These analyses are essential for ensuring the safety of a repository and allow comparisons of potential siting regions to ensure that the most suitable site is selected. Current activities include:
- Planning and management of petrophysical logging, microhydraulic fracturing, and vertical seismic profiling (VSP) campaigns.
- Wellsite supervision to ensure operations are carried out safely, efficiently, and in accordance with Swiss regulations
- Data management, quality assurance (QA), and quality control (QC)
- Advanced deterministic and stochastic petrophysical log evaluation
- Interpretation of MHF for full stress tensor determination, calibration & validation of 3D geomechanical models
- VSP processing and interpretation for the enhancement and correlation of 3D seismic surveys
For more information, please refer to the open access reports on each borehole below: